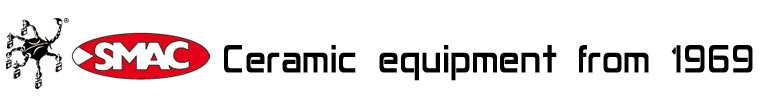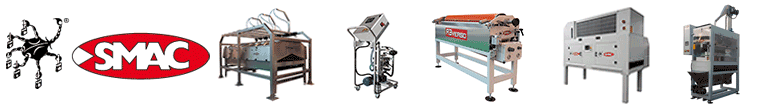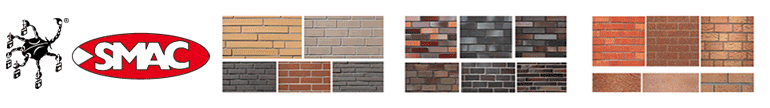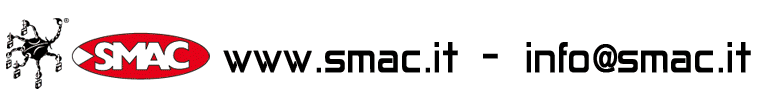Maincer technologies on display at Tecna 2024
At the Tecna exhibition in Rimini (24-27 September) Maincer presented its latest dry squaring machines for small-size tiles.
Producers of dry tile squaring technology have focused mainly on the medium- to large-size tile segment while largely neglecting small-size tiles. In response to numerous requests for tailored solutions from small- and medium-size tile manufacturers, Maincer has now developed a series of dry squaring machines tailored specifically to the needs of these smaller products.
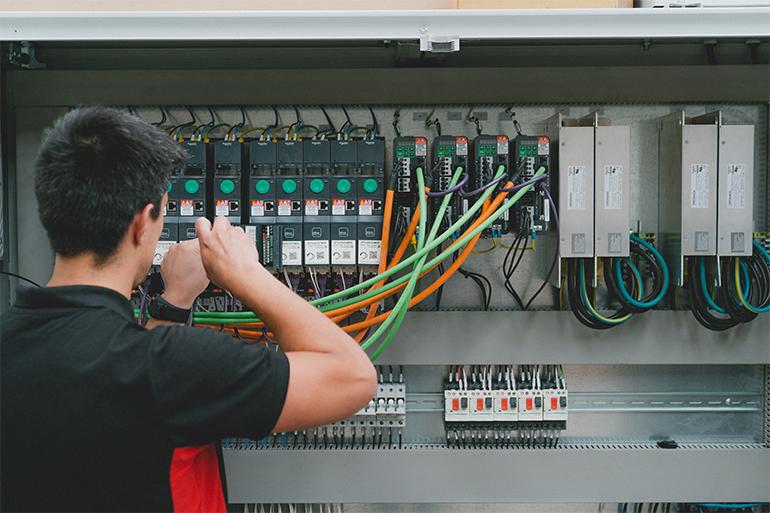
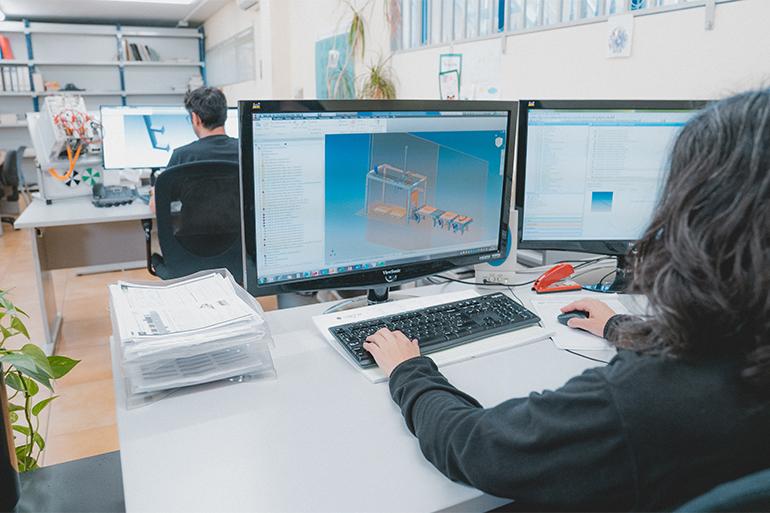
For over a decade, the Spanish company has been integrating automation and digitalisation into its technologies. With the advent of Industry 4.0, it has equipped its machines with sensors for real-time data collection and transfer to SCADA systems for monitoring and analysis. It has also invested in automation based on robots and automated production lines that operate synchronously without the need for human operators and has developed software to facilitate predictive maintenance, anticipate failures and enhance efficiency and productivity. These solutions not only improve efficiency and productivity but also reduce costs and downtime through predictive maintenance indicators.
Sustainability is another key priority for Maincer, which equips its machines with energy-efficient components such as variable-frequency drives and IE2 and IE3 motors. The company collaborates with Schneider Electric for the use of advanced monitoring systems such as EcoStruxure® Machine Advisor, enabling up to 30% energy savings through predictive maintenance. The squaring machines for both flatware and structural ceramics are equipped with inverters that optimise motor speed, thereby preventing current peaks and reducing wear.
Maincer has also adopted a number of measures to make its machines more sustainable:
- The water decanting and recirculation system enables water to be reused for diamond tool cooling, making the machine autonomous and eliminating the need for continuous water use.
- Dry technology is used wherever possible and the resultant dust extracted and reused.
- 3D printing has also been adopted to reduce the production of waste, to optimise the design of specific parts and to save raw materials.
Maincer participates in the Life EggShellence project, which uses eggshells as a secondary raw material in the manufacture of tiles. This project won a go!ODS award for the company’s commitment to sustainability and to meeting the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Among its future projects, the company is collaborating with a leading manufacturer of structural clay products to develop a machine for unifying the calibres of thermo-clay blocks. This machine automatically processes both sides of the block, ensuring uniformity and reducing the need for wide mortar joints, thereby speeding up the construction process and lowering material costs.



Did you find this article useful?
Join the CWW community to receive the most important news from the global ceramic industry every two weeks